Everything to know about Type 2 Diabetes
Type 1 and type 2 diabetes both occur when the body cannot properly store and use glucose, which is essential for energy. This glucose then collects in the blood and does not reach the cells that need it, leading to serious complications.
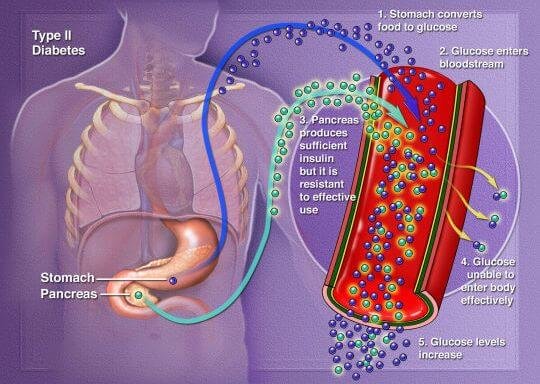
Type 2 diabetes is a condition that happens because of a problem in the way the body regulates and uses sugar as a fuel. That sugar also is called glucose. This long-term condition results in too much sugar circulating in the blood. Eventually, high blood sugar levels can lead to disorders of the circulatory, nervous and immune systems.
In type 2 diabetes, there are primarily two problems. The pancreas does not produce enough insulin — a hormone that regulates the movement of sugar into the cells. And cells respond poorly to insulin and take in less sugar.
Type 2 diabetes used to be known as adult-onset diabetes, but both type 1 and type 2 diabetes can begin during childhood and adulthood. Type 2 is more common in older adults. But the increase in the number of children with obesity has led to more cases of type 2 diabetes in younger people.
There’s no cure for type 2 diabetes. Losing weight, eating well and exercising can help manage the disease. If diet and exercise aren’t enough to control blood sugar, diabetes medications or insulin therapy may be recommended.
Symptoms
Symptoms of type 2 diabetes often develop slowly. In fact, you can be living with type 2 diabetes for years and not know it. When symptoms are present, they may include:
- Increased thirst.
- Frequent urination.
- Increased hunger.
- Unintended weight loss.
- Fatigue.
- Blurred vision.
- Slow-healing sores.
- Frequent infections.
- Numbness or tingling in the hands or feet.
- Areas of darkened skin, usually in the armpits and neck.
Causes

Type 2 diabetes is mainly the result of two problems:
- Cells in muscle, fat and the liver become resistant to insulin As a result, the cells don’t take in enough sugar.
- The pancreas can’t make enough insulin to keep blood sugar levels within a healthy range.
Exactly why this happens is not known. Being overweight and inactive are key contributing factors.
How insulin works
Insulin is a hormone that comes from the pancreas — a gland located behind and below the stomach. Insulin controls how the body uses sugar in the following ways:
- Sugar in the bloodstream triggers the pancreas to release insulin.
- Insulin circulates in the bloodstream, enabling sugar to enter the cells.
- The amount of sugar in the bloodstream drops.
- In response to this drop, the pancreas releases less insulin.
The role of glucose
Glucose — a sugar — is a main source of energy for the cells that make up muscles and other tissues. The use and regulation of glucose includes the following:
- Glucose comes from two major sources: food and the liver.
- Glucose is absorbed into the bloodstream, where it enters cells with the help of insulin.
- The liver stores and makes glucose.
- When glucose levels are low, the liver breaks down stored glycogen into glucose to keep the body’s glucose level within a healthy range.
In type 2 diabetes, this process doesn’t work well. Instead of moving into the cells, sugar builds up in the blood. As blood sugar levels rise, the pancreas releases more insulin. Eventually the cells in the pancreas that make insulin become damaged and can’t make enough insulin to meet the body’s needs.
Risk factors
Factors that may increase the risk of type 2 diabetes include:
- Weight. Being overweight or obese is a main risk.
- Fat distribution. Storing fat mainly in the abdomen — rather than the hips and thighs — indicates a greater risk. The risk of type 2 diabetes is higher in men with a waist circumference above 40 inches (101.6 centimeters) and in women with a waist measurement above 35 inches (88.9 centimeters).
- Inactivity. The less active a person is, the greater the risk. Physical activity helps control weight, uses up glucose as energy and makes cells more sensitive to insulin.
- Family history. An individual’s risk of type 2 diabetes increases if a parent or sibling has type 2 diabetes.
- Race and ethnicity. Although it’s unclear why, people of certain races and ethnicities — including Black, Hispanic, Native American and Asian people, and Pacific Islanders — are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes than white people are.
- Blood lipid levels. An increased risk is associated with low levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol — the “good” cholesterol — and high levels of triglycerides.
- Age. The risk of type 2 diabetes increases with age, especially after age 35.
- Prediabetes. Prediabetes is a condition in which the blood sugar level is higher than normal, but not high enough to be classified as diabetes. Left untreated, prediabetes often progresses to type 2 diabetes.
- Pregnancy-related risks. The risk of developing type 2 diabetes is higher in people who had gestational diabetes when they were pregnant and in those who gave birth to a baby weighing more than 9 pounds (4 kilograms).
- Polycystic ovary syndrome. Having polycystic ovary syndrome — a condition characterized by irregular menstrual periods, excess hair growth and obesity — increases the risk of diabetes.
Diagnosis
Type 2 diabetes is usually diagnosed using the glycated hemoglobin (A1C) test. This blood test indicates your average blood sugar level for the past two to three months. Results are interpreted as follows:
- Below 5.7% is normal.
- 5.7% to 6.4% is diagnosed as prediabetes.
- 6.5% or higher on two separate tests indicates diabetes.
- If the A1C test isn’t available, or if you have certain conditions that interfere with an A1C test, your health care provider may use the following tests to diagnose diabetes:
- Random blood sugar test. Blood sugar values are expressed in milligrams of sugar per deciliter (mg/dL) or millimoles of sugar per liter (mmol/L) of blood. Regardless of when you last ate, a level of 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) or higher suggests diabetes, especially if you also have symptoms of diabetes, such as frequent urination and extreme thirst.
- Fasting blood sugar test. A blood sample is taken after you haven’t eaten overnight. Results are interpreted as follows:
- Less than 100 mg/dL (5.6 mmol/L) is considered healthy.
- 100 to 125 mg/dL (5.6 to 6.9 mmol/L) is diagnosed as prediabetes.
- 126 mg/dL (7 mmol/L) or higher on two separate tests is diagnosed as diabetes.
- Oral glucose tolerance test. This test is less commonly used than the others, except during pregnancy. You’ll need to not eat for a certain amount of time and then drink a sugary liquid at your health care provider’s office. Blood sugar levels then are tested periodically for two hours. Results are interpreted as follows:
- Less than 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L) after two hours is considered healthy.
- 140 to 199 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L and 11.0 mmol/L) is diagnosed as prediabetes.
- 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) or higher after two hours suggests diabetes.
Credit: mayoclinic.org