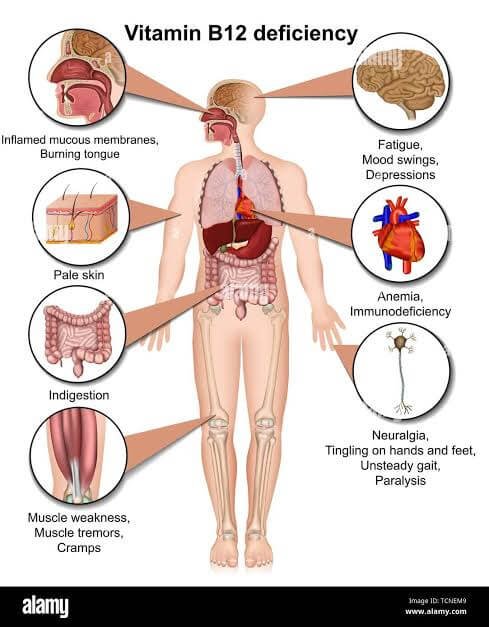
Vitamin B12 deficiency could result to a numerous disorders in human system yet not easily delineated.
Vitamin B12 plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, including red blood cell formation, neurological health, and DNA synthesis. Since the body cannot produce B12 on its own, it must be obtained through diet or supplements. Ignoring signs of B12 deficiency can lead to serious health issues over time. Here are a few signs of Vitamin B12 deficiency identifying which is essential.
Unexplained Tiredness
Persistent fatigue and weakness are common early signs of Vitamin B12 deficiency, as the vitamin is essential for energy production in the body. Fatigue is a symptom that can be attributed to various factors, and individuals often dismiss it as a consequence of a busy lifestyle, stress, or lack of sleep.
Neurological Disorders
Vitamin B12 is crucial for maintaining healthy nerve cells. Deficiency can result in neurological symptoms such as numbness, tingling, and difficulty walking. Neurological symptoms may develop gradually and be mistaken for other conditions, leading to delayed diagnosis and treatment.
Memory Loss
Vitamin B12 deficiency can impact cognitive function, leading to memory loss, difficulty concentrating, and mood changes. Cognitive changes may be attributed to aging or stress, and individuals may not immediately connect them to a nutritional deficiency.
Gastrointestinal Symptoms
Vitamin B12 deficiency can cause digestive issues such as diarrhea, constipation, and loss of appetite. Gastrointestinal symptoms are common and can be linked to various factors, making it challenging to recognize them as signs of B12 deficiency.
Pale Skin
Anemia resulting from B12 deficiency can lead to pale or yellowish skin. Changes in skin tone may be attributed to other factors, and individuals may not recognize them as indicative of a nutritional deficiency.
Gait Disorders
Vitamin B12 deficiency can affect coordination and balance, leading to difficulty walking and an increased risk of falls. Gait issues may be associated with aging or other neurological conditions, diverting attention from a potential B12 deficiency.
Causes of Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Individuals following a strict vegetarian or vegan diet may not get enough B12 from their food sources, as plant-based options are limited. Conditions affecting the stomach and intestines, such as atrophic gastritis, celiac disease, Crohn’s disease, and pernicious anemia, can interfere with the absorption of B12.
As people age, the production of stomach acid and intrinsic factors may decline, impacting B12 absorption. Certain medications, such as proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), H2 blockers, and metformin, can reduce B12 absorption. Surgical procedures involving the stomach or intestines, including weight loss surgeries, can limit the absorption of B12. This bacterial infection in the stomach can affect the stomach lining and reduce B12 absorption.
Vitamin B12 Complications
Vitamin B12 deficiency may contribute to psychiatric symptoms such as depression, anxiety, mood swings, and even psychosis. Damage to the peripheral nerves, known as peripheral neuropathy, can occur due to vitamin B12 deficiency.
This can lead to symptoms like tingling, numbness, and pain in the extremities. Severe deficiency can lead to damage to the optic nerve, resulting in optic neuropathy. This may lead to vision problems and even vision loss if not addressed promptly. B12 deficiency in pregnant women may lead to developmental issues in the fetus and an increased risk of neural tube defects. In men, deficiency can contribute to infertility and low sperm count.
Sources of Vitamin B12
A well-balanced diet must include sources of B12, such as meat, fish, dairy products, and eggs. Consider B12 supplements if following a vegetarian or vegan diet. B12 supplements are available in various forms, including oral tablets, sublingual tablets, and injections. Consult a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate dosage and form of supplementation.
Daily Vitamin B12 Requirement
The recommended daily intake of vitamin B12 for adults is approximately 2.4 micrograms. However, individuals with certain conditions, such as pernicious anemia or gastrointestinal disorders, may require higher doses or supplementation. Dietary sources of B12 include meat, fish, dairy, and fortified foods.
Credit: timesofindia.com